How is the heart operated on? Heart surgery: necessary recommendations. Complications and consequences of the operation
May God grant everyone to live a long life so that the surgeon's scalpel never touches his heart. However, not always cardiac surgery can be replaced by therapy.
When is surgery necessary?
- When conservative therapy does not give the desired result.
- When, despite all the ongoing treatment, the patient's condition continues to deteriorate.
- When there are severe congenital heart defects, severe arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy.
By urgency, cardiosurgical operations are emergency and planned.
- Emergencies are carried out when a person's life is in serious danger. This happens when a myocardial infarction occurs, a blood clot suddenly breaks off, or aortic dissection begins. They do not tolerate delay in surgery when the heart is injured. The consequences of delay are severe.
- Planned are carried out in accordance with the developed plan for the correction of the patient's health. The date of the operation may be postponed depending on the circumstances. For example: with a cold, to avoid additional stress on the heart, or when the pressure suddenly dropped.
Surgical intervention differs in the technique of execution. There are such types of heart operations:
- with the opening of the chest;
- without opening the chest.
Chest opening operations
Such surgical intervention is used in especially severe cases, when full accessibility of the heart is required during the operation.
Opening of the chest is performed with such pathologies:
- tetralogy of Fallot (the so-called congenital heart disease with four serious violations of the anatomical structure);
- serious anomalies of intracardiac partitions, valves, aorta and coronary arteries;
- heart tumors.
The patient arrives at the hospital one day before the operation. Passes inspection, gives written consent. Be sure to wash with antibacterial soap and shave your hair. Where do you shave your body hair? The hair will be shaved at the site of the proposed incision. If you are going to have a coronary bypass surgery, you will have to shave your legs and groin. In the case of a heart valve replacement, it is necessary to shave the hair in the lower abdomen and in the groin area.
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. To gain access to the heart, the surgeon opens the chest of the person being operated on. The patient is connected to an artificial lung ventilation apparatus, the heart stops for a while and surgical manipulations are performed with the organ.
How long the operation takes depends on the severity of the pathology. On average, several hours.
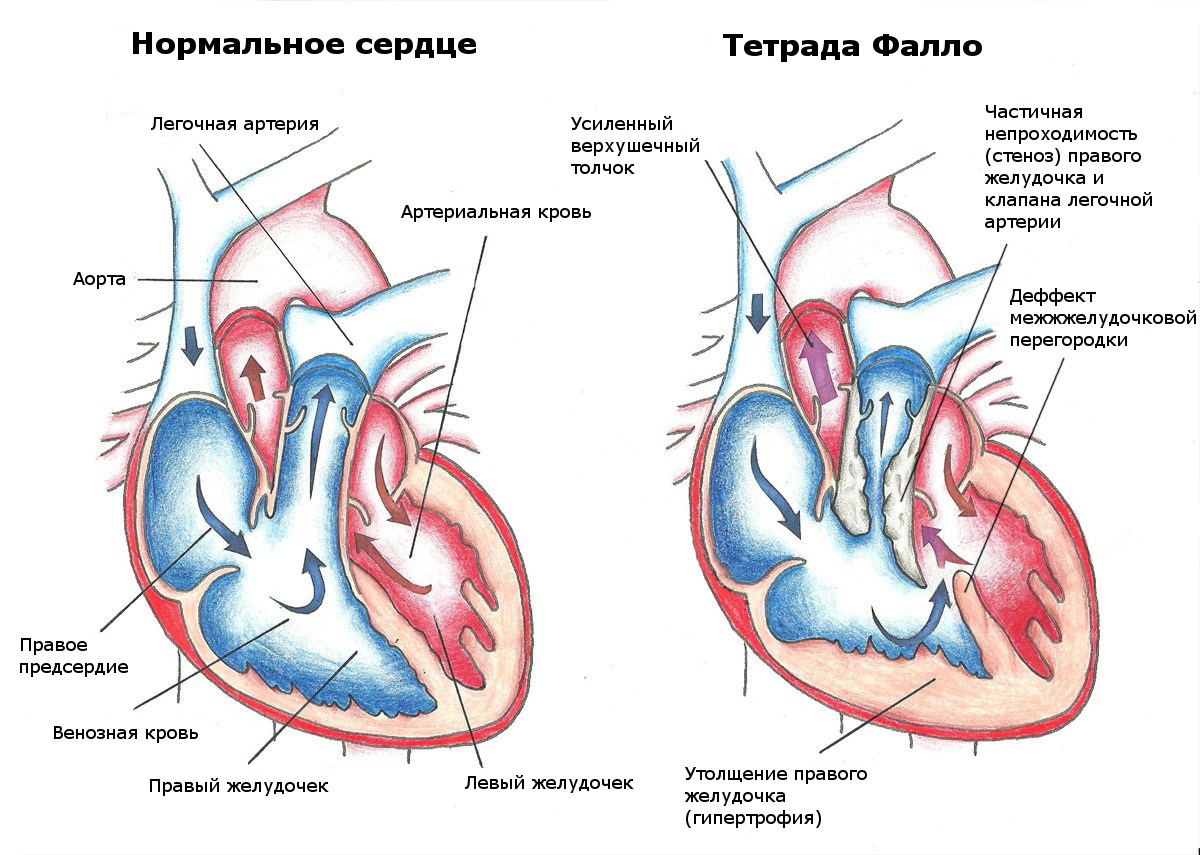 Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot Open heart surgery has two advantages.
- The surgeon has full access to the patient's heart.
- Such a surgical intervention is possible without state-of-the-art medical equipment.
However, there are also significant drawbacks.
- Surgical manipulations with the heart last several hours, which leads to fatigue of the operating team, during the operation there is a higher probability of making an erroneous action.
- Opening the chest is fraught with various injuries.
- There is a noticeable scar after heart surgery.
- Various complications are not excluded:
- myocardial infarction,
- thromboembolism,
- bleeding,
- infections;
- coma after surgery.
- A long recovery is required with significant limitations in the patient's activities.
In most cases, when surgery is performed with an opening of the chest, disability is given after heart surgery, as after a heart attack.
What operations and under what pathologies are performed on the open heart?
Pathologies of the coronary arteries
Coronary artery bypass grafting is done in case of serious atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary arteries, which led to a severe form of coronary heart disease. The essence of shunting is to create a bypass for blood flow to the heart using a shunt, for which an artery or vein taken from the patient is used. For example: mammary coronary artery bypass grafting (MCB) is performed using the internal mammary (mammary) artery.
 Operation Ross
Operation Ross Heart valve defects
Today, valves made from the patient's biological material are used to replace damaged valves.
- The Ross procedure involves using the patient's own valvular pulmonary artery to replace a diseased aortic valve. An implant is placed in place of the pulmonary valve. Eliminates complications associated with rejection of a valve made of foreign material. Made for both adults and children.
- The Ozaki operation involves the use of the patient's own tissue. Only in this case, the replacement of the aortic valve is performed with a valve made from the patient's pericardium. Complications with valve rejection are not observed for the same reason.
- Heart valve replacement
- Possible complications and recommendations for care
Heart surgery is performed only when necessary. The most common of these are heart valve replacement and coronary artery bypass grafting. The first is necessary if the patient is concerned about valvular stenosis. It should be noted that heart surgeries pose a serious risk to the life of the patient, they are carried out with maximum precision and caution. Heart surgery sometimes leads to numerous problems and complications, in order to avoid this, you can use an alternative technique - valvuloplasty.
The procedure can replace replacement surgery, help normalize the activity of the heart muscles. In the process, a special balloon is inserted into the opening of the aortic valve, at the end this balloon is inflated. It is worth considering: if a person is in old age, valvuloplasty does not give a lasting effect.
Heart valve replacement
To decide on such a procedure, it is necessary to establish a diagnosis.
The operation is carried out immediately or some time after the test.
In some situations, the results indicate that a person needs bypass surgery. Valve replacement is an open procedure that can be performed using minimally invasive surgery. It should be remembered that heart valve replacement is a very complicated procedure, despite this, it is carried out very often.
Back to index
Stages of the procedure and further rehabilitation
 First you need to open the chest. Next, the doctor connects the patient to a special apparatus that provides artificial circulation. The device temporarily replaces the heart. The patient's circulatory system is connected to the device, after which the natural valve is removed and replaced. When this manipulation is completed, the device is turned off. In most cases, heart surgery goes well, but a scar forms on the organ.
First you need to open the chest. Next, the doctor connects the patient to a special apparatus that provides artificial circulation. The device temporarily replaces the heart. The patient's circulatory system is connected to the device, after which the natural valve is removed and replaced. When this manipulation is completed, the device is turned off. In most cases, heart surgery goes well, but a scar forms on the organ.
After recovery from anesthesia, the breathing tube is removed from the lungs. If you want to remove excess fluid, such a tube should be left for a while. After a day, it is allowed to drink water and liquid, you can walk only after two days. After such an operation, pain in the chest area can be felt, and on the fifth day the patient is completely discharged. If there is a risk of complications, the hospital stay must be extended by 6 days.
Back to index
Can there be complications after valve replacement?
A person can face such problems at different stages of the disease. During the operation, there is a risk of heavy bleeding, in addition, difficulties with anesthesia may arise. Possible risk factors include internal bleeding, seizures, possible infections. A heart attack can also happen, but this happens very rarely. As for the greatest danger, it lies in the appearance of tamponade of the pericardial cavity. This phenomenon occurs when blood fills its heart sac. This causes serious malfunctions in the functioning of the heart. Operations on the heart cannot but affect the general condition of a person. During the rehabilitation period, strict medical supervision is required. The need to visit the surgeon arises after 3-4 weeks after the operation. It is important to maintain the general well-being of the patient. An optimal dose of physical activity should be prescribed, it is important to stick to a diet.
Back to index
What is coronary artery bypass grafting?
 Coronary artery bypass grafting is a type of surgery that restores blood flow in the arteries. The procedure is necessary to eliminate coronary heart disease. The disease manifests itself when the lumen of the coronary vessels narrows, as a result of which an insufficient amount of oxygen enters the heart muscle. Coronary artery bypass surgery aims to prevent changes in the myocardium (heart muscle). After the operation, he should fully recover and contract better. It is necessary to restore the affected area of the muscle, for this the following procedure is carried out: everyday shunts are applied between the aorta and the coronary vessel that is affected. Thus, the formation of new coronary arteries occurs. They are designed to replace the narrowed ones. After the shunt is applied, blood from the aorta flows through a healthy vessel, thanks to which the heart produces a normal blood flow.
Coronary artery bypass grafting is a type of surgery that restores blood flow in the arteries. The procedure is necessary to eliminate coronary heart disease. The disease manifests itself when the lumen of the coronary vessels narrows, as a result of which an insufficient amount of oxygen enters the heart muscle. Coronary artery bypass surgery aims to prevent changes in the myocardium (heart muscle). After the operation, he should fully recover and contract better. It is necessary to restore the affected area of the muscle, for this the following procedure is carried out: everyday shunts are applied between the aorta and the coronary vessel that is affected. Thus, the formation of new coronary arteries occurs. They are designed to replace the narrowed ones. After the shunt is applied, blood from the aorta flows through a healthy vessel, thanks to which the heart produces a normal blood flow.
Back to index
What is the operation for?
This procedure will be required if the left coronary artery of the vessel that provides flow to the heart is affected. It is also needed if all coronary vessels are damaged. The procedure can be double, triple, single - it all depends on how many shunts the doctor needs. With coronary heart disease, the patient may need one shunt, in some cases two or three. Bypass surgery is a procedure that is often used for atherosclerosis of the heart vessels. This happens when angioplasty is not possible. As a rule, a shunt can serve for a long time, its functional suitability is 12-14 years.
Back to index
Carrying out coronary artery bypass grafting
 The duration of the operation is 3-4 hours. The procedure requires maximum concentration and attention. The doctor needs to gain access to the heart, for this it is necessary to dissect the soft tissues, then open the sternum and perform a stenotomy. During the operation, a procedure is carried out that is necessary for temporary, it is called cardioplegia. The heart must be cooled with very cold water, then a special solution should be injected into the arteries. To attach shunts, the aorta must be temporarily blocked. To do this, it is necessary to pinch it and connect the heart-lung machine for 90 minutes. Plastic tubes should be placed in the right atrium. Next, the doctor performs procedures that contribute to the flow of blood into the body.
The duration of the operation is 3-4 hours. The procedure requires maximum concentration and attention. The doctor needs to gain access to the heart, for this it is necessary to dissect the soft tissues, then open the sternum and perform a stenotomy. During the operation, a procedure is carried out that is necessary for temporary, it is called cardioplegia. The heart must be cooled with very cold water, then a special solution should be injected into the arteries. To attach shunts, the aorta must be temporarily blocked. To do this, it is necessary to pinch it and connect the heart-lung machine for 90 minutes. Plastic tubes should be placed in the right atrium. Next, the doctor performs procedures that contribute to the flow of blood into the body.
What is routine vascular bypass surgery? This method involves the implantation of special implants into the coronary vessels outside the obstruction, the end of the shunt is sutured to the aorta. In order to be able to use the internal mammary arteries, it is necessary to carry out the procedure with the expenditure of more time. This is due to the need to separate the arteries from the chest wall. Upon completion of the operation, the doctor carefully fastens the chest, for this a special wire is used. With its help, a soft tissue incision is sutured, then drainage tubes are applied to remove residual blood.
Sometimes bleeding occurs after the operation, it continues throughout the day. The installed drainage tubes should be removed after 12-17 hours after the procedure. At the end of the operation, the breathing tube must be removed. On the second day, the patient can get out of bed and move around. Restoration of the heart rhythm takes place in 25% of patients. As a rule, it lasts for five days. As for arrhythmia, this disease can be eliminated within 30 days after surgery, for this conservative methods of therapy are used.
Operations on the heart and blood vessels are performed by such a branch of medicine as cardiac surgery.
With the help of cardiac surgeons, many vascular and cardiac diseases can be effectively treated, thereby significantly prolonging the life of the patient.
Operations on the heart and blood vessels can significantly improve the general well-being of the patient.
They should be performed only after a thorough diagnosis and preparation of the patient.
It is very important to follow all the instructions of the specialist exactly.
Regardless of what kind of disease was detected in a person, there are the following general indications for operations on the heart and blood vessels:
- Rapid deterioration of the patient's condition and progression of the underlying disease of the heart or blood vessels.
- The lack of positive dynamics from the use of traditional drug therapy, that is, when taking pills no longer helps a person to maintain his condition in a normal way.
- The presence of acute signs of deterioration of the underlying myocardial disease, which cannot be eliminated by conventional analgesics or antispasmodics.
- The neglect of the underlying disease, in which the patient hesitated to contact the doctor, which led to very severe symptoms of the disease.
These procedures are indicated for patients with heart defects (regardless of whether they are congenital or acquired). Moreover, thanks to current techniques, this disease can be treated even in newborn babies, thereby providing them with a healthy life.
The next common indication is myocardial ischemia. In this case, surgery may be required when the underlying disease is aggravated by a heart attack. In this condition, the sooner surgery is performed, the greater the chance that the person will survive.
A significant indication for the need for surgical intervention can be acute heart failure, which provokes abnormal contraction of the myocardial ventricles. At the same time, it is important that the patient prepares for the operation in advance (to avoid postoperative complications in the form of a blood clot).
Often, surgery is required for myocardial valve disease, which was triggered by trauma or an inflammatory process. Rarely, other causes contribute to its appearance.
A serious reason for the urgent intervention of surgeons is the diagnosis of narrowing of the coronary valve of the artery, as well as endocarditis of infectious origin.
Additional conditions that may require a person to have myocardial surgery include:
- Severe aortic aneurysm, which may result from trauma or be congenital.
- Rupture of the ventricle of the heart, because of which the blood flow was disturbed.
- Various types of arrhythmias that can be eliminated by inserting or replacing an already installed pacemaker. They are commonly used for atrial fibrillation and bradycardia.
- Diagnosis of an obstruction in the myocardium in the form of tamponade, due to which the heart cannot pump the required volume of blood normally. This condition can occur under the influence of viral infections, acute tuberculosis and heart attack.
- Acute insufficiency of the left ventricles of the myocardium.
Cardiac surgery is not always necessary for the above indications. Each case is individual and only the attending physician can decide what is best for a particular patient - traditional drug therapy or a planned (urgent) operation.
In addition, it should be noted that heart surgery may be required in case of exacerbation of the underlying disease, as well as if the first surgical intervention did not give the expected results. In this case, the patient may need to repeat manipulation. Its cost and preparation features (diet, medication) depend on the complexity of the operation.
Surgical interventions can be practiced both on the open myocardium and on the closed one, when the heart and its cavity are not completely affected. The first type of operations involves dissection of the chest and connecting the patient to artificial respiration equipment.

During open-type operations, surgeons artificially stop the heart for a while, so that within a few hours they can perform the necessary surgical procedures on the organ. These interventions are considered very dangerous and traumatic, but even very complex myocardial diseases can be eliminated with their help.
Closed type operations are more secure. They are usually used to correct minor heart and vascular defects.
There are the following most common types of myocardial operations, which are most often practiced in cardiac surgery:
- Installation of artificial valves.
- Operations according to the method of Glenn and Ross.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting and stenting of arteries.
- Ablation of radiofrequency type.
An operation called radiofrequency ablation is a low-traumatic procedure that allows you to achieve significant improvements in heart failure and various types of arrhythmias. It rarely causes side effects and is well tolerated by patients.
RA is performed using special catheters that are inserted under X-ray control. The patient is then given local anesthesia. During this operation, a catheter is inserted into the organ and, thanks to electrical impulses, the normal heart rhythm is restored to the person.
The next type of surgery is prosthetic heart valves. This intervention is very often practiced, since such a pathology as myocardial valve insufficiency is extremely common.
It should be noted that in the event of a severe failure in the patient's heart rhythm, he may need to install a special device - a pacemaker. It is needed to normalize the rhythm of the heart.
When prosthetic heart valves can be used the following types of implants:
- Mechanical prostheses that are made of metal or plastic. They serve for a very long time (for several decades), however, they require a person to constantly take drugs to thin the blood, because due to the introduction of a foreign object in the body, a tendency to form blood clots actively develops.
- Biological implants are made from animal tissues. They are very durable and do not require special preparations. Despite this, patients after a couple of decades often require a second operation.
Glenn and Ross operations are commonly used to treat children with congenital myocardial defects. The essence of these interventions is to create a special connection for the pulmonary artery. After this operation, the child can live for a long time, with little or no need for maintenance therapy.
During the Ross operation, the patient is replaced by a diseased myocardial valve with a healthy one, which will be removed from his own pulmonary valve.
Cardiac bypass surgery: indications and conduct
 Coronary artery bypass grafting is a surgical intervention on the heart, during which an additional vessel is sewn in order to restore the disturbed blood supply in the clogged blood arteries.
Coronary artery bypass grafting is a surgical intervention on the heart, during which an additional vessel is sewn in order to restore the disturbed blood supply in the clogged blood arteries.
Cardiac bypass surgery is practiced when the narrowed vessels of the patient are no longer amenable to drug treatment and the blood cannot circulate normally in the heart, causing ischemic attacks.
A direct indication for cardiac bypass surgery is acute coronary aortic stenosis. Most often, a neglected form of atherosclerosis leads to its development, which contributes to clogging of blood vessels with cholesterol plaques.
Due to vasoconstriction, blood cannot circulate normally and deliver oxygen to myocardial cells. This leads to its defeat and the risk of a heart attack.
Today, heart vessel bypass surgery can be performed both on a beating heart and on an artificially stopped one. At the same time, it should be noted that if shunting is done on a working myocardium, then the likelihood of postoperative complications is much higher than when performing a procedure on a stopped myocardium.
The course of this operation consists in blocking the main aorta and implanting artificial vessels into the affected coronary arteries. Usually, a vessel in the leg is used for shunting. It is used as a biological implant.
Contraindications to this surgical intervention may be an existing pacemaker or an artificial valve in the heart, the functions of which may be impaired during such an operation. In general, the need for shunting is determined individually by the doctor for each individual patient, based on the diagnostic data and the patient's symptoms.
After bypass surgery, the recovery period is usually fast, especially if the patient does not have any complications after the procedure. Within a week after the operation, the patient must comply with bed rest. Until the stitches are removed, a person needs to do wound dressings daily.

After ten days, a person can get out of bed and begin to perform simple movements of physiotherapy exercises in order to restore the body.
After the wound has completely healed, the patient is advised to go swimming and walk regularly in the fresh air.
It should be noted that the wound after shunting is not sewn with threads, but with special metal staples.. This is justified by the fact that the dissection falls on a large bone, so it needs to grow together as carefully as possible and ensure peace.
To make it easier for a person to move around after the operation, he is allowed to use special medical support bandages. They look like a corset and perfectly support the seams.
After surgery, due to blood loss, a person may experience anemia, which will be accompanied by weakness and dizziness. To eliminate this condition, the patient is advised to eat right and enrich his diet with beets, nuts, apples and other fruits.
To reduce the likelihood of re-constriction of blood vessels, alcohol, fatty and fried foods should be completely excluded from the menu.
The operation of stenting of the vessels of the heart: indications and features of the conduct
Arterial stenting is a low-traumatic angioplasty procedure, which involves the imposition of a stent into the lumen of the affected vessels.
The stent itself is similar to a conventional spring. It is injected into the vessel after it has been artificially dilated.
Indications for cardiac stenting surgery are:
- IHD (ischemic heart disease), which leads to impaired blood circulation and oxygen starvation of the myocardium.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Clogging of blood vessels with cholesterol plaques, which lead to a narrowing of their lumen.
Additional contraindications to this procedure are the patient's individual intolerance to iodine, which is invariably used during stenting, as well as the case when the total size of the diseased artery is less than 2.5 mm (in this case, the surgeon simply cannot install the stent).

An operation is performed to stent the vessels of the heart by introducing a special balloon that will expand the lumen of the diseased vessel. Further, a filter is installed in this place, which prevents subsequent blood clots and stroke.
After that, a stent is inserted into the vessel; it will support the vessel from narrowing, serving as a certain frame.
The surgeon monitors the entire course of the operation through a monitor. At the same time, he will see the stent and the vessel well, since even at the beginning of the procedure, the patient is injected with an iodine solution, which will reflect all the actions of the surgeon.
The advantage of stenting is that this operation has a low risk of complications. Moreover, it is performed under local anesthesia and does not require a long period of hospitalization.
After stenting, the patient must remain in bed for a certain time (usually for a week). After that, if there are no complications, the person is allowed to go home.
It is very important to exercise regularly after this operation. At the same time, it is worth controlling your condition and not allowing physical overwork.
Every two weeks after the procedure, the patient must necessarily come to the doctor and undergo a follow-up examination. When pain occurs, a person should immediately report it to the doctor.
To recover faster, the patient should take all the drugs prescribed by the doctor. Sometimes drug therapy lasts a long time, more than one month in a row.

Be sure to follow a dietary diet after stenting.
It provides for the following:
- Complete abstinence from alcohol and smoking.
- Ban on all animal fats. Also, you can not eat caviar, chocolate, fatty meat and sweet confectionery.
- The basis of the diet should be vegetable soups, fruit mousses, cereals and greens.
- You need to eat at least six times a day, but at the same time, portions should not be large.
- You should completely limit the consumption of salt and salted fish.
- It is important to drink plenty of fluids to maintain normal water balance in the body. It is recommended to drink fruit compotes, juices and green tea. You can also use a rosehip decoction.
In addition, a person needs to control their blood pressure and blood sugar levels. This is especially important in the presence of already existing hypertension and diabetes, because these diseases can worsen the functioning of the heart.
Cardiac surgery is a branch of medicine dedicated to the surgical treatment of the heart. With pathologies of the cardiovascular system, such intervention is an extreme measure. Doctors try to restore the patient's health without surgery, but in some cases only cardiac surgery can save the patient. Today, this field of cardiology uses the latest advances in science to return the patient to health and a fulfilling life.
Indications for operations
Invasive interventions on the heart is a complex and risky job, it requires skill and experience, and the patient - preparation and implementation of recommendations. Since such operations are risky, they are carried out only when absolutely necessary. In most cases, the patient is trying to rehabilitate with the help of medicines and medical procedures. But in cases where such methods do not help, heart surgery is needed. Surgical intervention is carried out in a hospital and complete sterility, the operated is under anesthesia and the control of the surgical team.
Such interventions are needed for congenital heart defects or acquired. The former include pathologies in the anatomy of the organ: defects in valves, ventricles, impaired blood circulation. Most often they are discovered even during the bearing of a child. Heart disease is also diagnosed in newborns, often such pathologies need to be eliminated urgently in order to save the life of the baby. Among the acquired diseases, ischemic disease is in the lead, in this case, surgery is considered the most effective method of treatment. Also in the heart area there are: impaired blood circulation, stenosis or valve insufficiency, heart attack, pericardial pathology and others.
Heart surgery is prescribed in situations where conservative treatment does not help the patient, the disease progresses rapidly and threatens life, with pathologies that require urgent and urgent correction, and in advanced forms of diseases, a late visit to the doctor.
The decision on the appointment of the operation is made by a council of doctors or. The patient must be examined to establish an accurate diagnosis and type of surgical intervention. They identify chronic diseases, stages of the disease, assess the risks, in which case they talk about a planned operation. If emergency assistance is needed, for example, when a blood clot is torn off or an aneurysm is exfoliated, minimal diagnostics are performed. In any case, the function of the heart is restored surgically, its departments are rehabilitated, blood flow and rhythm are normalized. In severe situations, the organ or its parts are no longer amenable to correction, then prosthetics or transplantation is prescribed.
Classification of heart operations
 In the area of the heart muscle, there can be dozens of different diseases, these are: insufficiency, narrowing of the lumen, ruptures of blood vessels, stretching of the ventricles or atria, purulent formations in the pericardium, and much more. To solve each problem, surgery has several types of operations. They are distinguished by urgency, effectiveness and method of influencing the heart.
In the area of the heart muscle, there can be dozens of different diseases, these are: insufficiency, narrowing of the lumen, ruptures of blood vessels, stretching of the ventricles or atria, purulent formations in the pericardium, and much more. To solve each problem, surgery has several types of operations. They are distinguished by urgency, effectiveness and method of influencing the heart.
The general classification divides them into operations:
- Buried - used to treat arteries, large vessels, aorta. During such interventions, the chest of the operated person is not opened, the heart itself is also not affected by the surgeon. Therefore, they are called "closed" - the heart muscle remains intact. Instead of a strip opening, the doctor makes a small incision in the chest, most often between the ribs. Closed types include: shunting, balloon angioplasty, stenosis of blood vessels. All these manipulations are designed to restore blood circulation, sometimes they are prescribed to prepare for a future open operation.
- Open - carried out after opening the sternum, sawing the bones. The heart itself during such manipulations can also be opened to get to the problem area. As a rule, for such operations, the heart and lungs must be stopped. To do this, connect the heart-lung machine - AIC, it compensates for the work of "disabled" organs. This allows the surgeon to accurately perform the work, in addition, the procedure under the control of AIC takes longer, which is necessary when eliminating complex pathologies. During open operations, AIC may not be connected, but only the desired zone of the heart can be stopped, for example, during coronary artery bypass grafting. Opening the chest is necessary to replace valves, prosthetics, and eliminate tumors.
- X-ray surgery - similar to a closed type of operation. The essence of this method is that the doctor moves a thin catheter through the blood vessels, and gets to the very heart. The chest is not opened, the catheter is placed in the thigh or shoulder. The catheter is injected with a contrast agent that stains the vessels. The catheter is advanced under X-ray control, the video image is transmitted to the monitor. Using this method, the lumen in the vessels is restored: at the end of the catheter there is a so-called balloon and a stent. At the site of narrowing, this balloon is inflated with a stent, restoring the normal patency of the vessel.
The safest are minimally invasive methods, that is, X-ray surgery and a closed type of surgery. With such work, the risk of complications is the least, the patient recovers faster after them, but they can not always help the patient. Complex operations can be avoided with periodic inspections. The earlier the problem is identified, the easier it is for the doctor to solve it.
 Depending on the condition of the patient, there are:
Depending on the condition of the patient, there are:
- planned operation. It is carried out after a detailed examination, within the agreed time frame. A planned intervention is prescribed when the pathology does not pose a particular danger, but it cannot be postponed.
- Urgent - these are operations that need to be done in the next few days. During this time, the patient is prepared, all the necessary studies are carried out. The date is set immediately after receiving the necessary data.
- Emergency. If the patient is already in serious condition, the situation may worsen at any time - an operation is prescribed immediately. Before her, only the most important examinations and preparations are carried out.
In addition, surgical care can be radical or auxiliary. The first implies the complete elimination of the problem, the second - the elimination of only part of the disease, improving the patient's well-being. For example, if a patient has a pathology of the mitral valve and stenosis of a vessel, the vessel is first restored (auxiliary), and after a while valve plastic surgery (radical) is prescribed.
How operations are done
The course and duration of the operation depends on the pathology being eliminated, the patient's condition, and the presence of concomitant diseases. The procedure can take half an hour, and can stretch for 8 hours or more. Most often, such interventions last 3 hours, are carried out under general anesthesia and AIC control. First, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound of the chest, urine and blood tests, an ECG, and a consultation with specialists. After receiving all the data, they determine the degree and place of the pathology, decide whether there will be an operation.
As part of the preparation, a low-fat, spicy, and fried diet is also prescribed. For 6-8 hours before the procedure, it is recommended to refuse food and drink less. In the operating room, the doctor assesses the well-being of the ward, introduces the patient into a medical sleep. With minimally invasive interventions, local anesthesia is sufficient, for example, during X-ray surgery. When anesthesia or anesthesia takes effect, the main actions begin.
Heart valve repair
There are four valves in the heart muscle, all of which serve as a passage for blood from one chamber to another. The most commonly operated valves are the mitral and tricuspid valves, which connect the ventricles to the atria. Stenosis of the passages occurs with insufficient expansion of the valves, while the blood does not flow well from one department to another. Valve insufficiency is a poor closure of the cusps of the passage, while there is an outflow of blood back.
 Plastic surgery is carried out open or closed, during the operation, special rings or sutures are applied manually along the diameter of the valve, which restore the normal lumen and narrow the passage. Manipulations last an average of 3 hours; with open views, an AIC is connected. After the procedure, the patient remains under the supervision of doctors for at least a week. The result is normal blood circulation and functioning of the heart valves. In severe cases, native leaflets are replaced with artificial or biological implants.
Plastic surgery is carried out open or closed, during the operation, special rings or sutures are applied manually along the diameter of the valve, which restore the normal lumen and narrow the passage. Manipulations last an average of 3 hours; with open views, an AIC is connected. After the procedure, the patient remains under the supervision of doctors for at least a week. The result is normal blood circulation and functioning of the heart valves. In severe cases, native leaflets are replaced with artificial or biological implants.
Elimination of heart defects
In most cases, defects are congenital, the cause of this can be hereditary pathologies, bad habits of parents, infections and fever during pregnancy. At the same time, children may have various anatomical abnormalities in the region of the heart, often such anomalies are poorly compatible with life. The urgency and type of surgery depends on the condition of the child, but they are often prescribed as early as possible. For children, heart surgery is performed only under general anesthesia, and under the supervision of medical equipment.
At an older age, heart defects develop with defects in the interatrial septum. This happens with mechanical damage to the chest, infectious diseases, due to concomitant heart disease. To eliminate such a problem, an open operation is also needed, more often with artificial cardiac arrest.
During manipulations, the surgeon can “patch” the septum with a patch, or suture the defective part.
Shunting
Coronary artery disease (CHD) is a very common pathology that affects mainly the generation over 50 years of age. Appears due to impaired blood flow in the coronary artery, which leads to oxygen starvation of the myocardium. There is a chronic form, in which the patient has constant attacks of angina pectoris, and an acute one is a myocardial infarction. They try to eliminate chronic pain conservatively or with the help of minimally invasive techniques. Acute requires urgent intervention.
To prevent complications or alleviate the disease, apply:
- aorto-coronary bypass;
- balloon angioplasty;
- transmyocardial laser revascularization;
- stenting of a coronary artery.
 All these methods are aimed at restoring normal blood flow. As a result, enough oxygen is supplied to the myocardium with blood, the risk of a heart attack is reduced, and angina pectoris is eliminated.
All these methods are aimed at restoring normal blood flow. As a result, enough oxygen is supplied to the myocardium with blood, the risk of a heart attack is reduced, and angina pectoris is eliminated.
If you need to restore normal patency, angioplasty or stenting is enough, in which the catheter is moved through the vessels to the heart. Before such an intervention, coronary angiography is performed to accurately determine the blocked area. Sometimes blood flow is restored bypassing the affected area, while a bio-shunt (often a section of the patient's own vein from the arm or leg) is sutured to the artery.
Recovery after interventions
After surgery, the patient remains in the hospital for another 1-3 weeks, all this time the doctors will assess his condition. The patient is discharged after verification and approval by the cardiologist.
The first month after surgical procedures is called the early postoperative period, at this time it is very important to follow all the doctor's recommendations: diet, calm and measured lifestyle. Nicotine, alcohol, junk food and physical activity are prohibited regardless of the type of intervention.
The doctor's recommendations should also contain a warning about the dangers and complications. At discharge, the doctor will set the date for the next appointment, but you need to seek help and unscheduled if the following symptoms occur:
- sudden fever;
- redness and swelling at the incision site;
- discharge from the wound;
- persistent chest pain;
- frequent dizziness;
- nausea, bloating and stool disorders;
- breathing difficulties.
At scheduled examinations, the cardiologist will listen to the heartbeat, measure the pressure, and listen to complaints. To check the effectiveness of the operation, ultrasound, computed tomography, x-ray examinations are prescribed. Such visits are scheduled once a month for six months, then the doctor will see you once every 6 months.
Often, in addition to surgical care, medications are prescribed. For example, when prosthetic valves are artificially implanted, the patient drinks anticoagulants for life.
In the postoperative period, it is important not to self-medicate, since the interaction of permanent drugs and other medications can give a negative result. Even conventional painkillers need to be discussed with. To keep fit and restore health faster, it is recommended to be outdoors more often, walk on foot.
Life after heart surgery will gradually return to its previous course, a full recovery is predicted within a year.
Cardiac surgery offers many methods for the rehabilitation of the heart. Such operations are designed to restore the patient's physical and moral strength. You should not be afraid or avoid such procedures, on the contrary, the sooner they are carried out, the greater the chances of success.
But now, the diagnosis has been made and the doctors understand what needs to be done next. I would like you to understand well by this moment, what will be discussed when they will explain everything in detail to you, what was found during the examination, what diagnosis was made, what needs to be done and when to choose the best way of treatment.
Here and now the main questions are being decided, and you must exactly imagine what you want to know before you make a decision on which a lot depends.
There are several options for conversation.
- You will be offered operation, as the only way out, and doctors believe that it needs to be done urgently.
- You are offered an operation, but they say that it can be postponed for a while.
- You are denied an operation for a variety of reasons.
You need to understand what is being said and prepare for the conversation. Try to be calm and confident in yourself and in the doctors who want to help you. You must be together, on the same side, in the fight for the future of the child. Discuss everything, but your questions should be literate. Believe me, a lot depends on this too.
What do you need to know about in order to ask the right question? What are the operations? What should the child do? How will it all be? Who will do it? Let's talk about it calmly.
Today, all interventions, or operations, for congenital heart defects can be divided into three categories: "closed" operations, "open" and "X-ray surgery".
✔ Closed Operations These are surgical interventions in which the heart itself is not affected. They are performed outside of it, and therefore do not require the use of any special equipment other than conventional surgical instruments. The cavities of the heart are not “opened” with them, which is why they are called “closed”, and they are widely performed as the first stage of surgical intervention.
✔ Open Operations- These are surgical interventions in which it is necessary to open the cavities of the heart in order to eliminate the existing defect. For this, a special apparatus is used - a heart-lung machine (AIC), or "heart-lungs". For the period of the operation, both the heart and the lungs are switched off from the circulation, and the surgeon gets the opportunity to perform any operation on the so-called "dry", stopped heart.
All the patient's venous blood is sent to the apparatus, where, passing through an oxygenator (artificial lung), it is saturated with oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide, turning into arterial. Then the arterial blood is pumped into the patient's aorta by a pump, i.e. into the systemic circulation. Modern technologies allow all the internal parts of the device (including the oxygenator), with which the patient's blood comes into contact, to be made "disposable", i.e. use them only once and only for one patient. This dramatically reduces the number of possible complications.
Today, thanks to AIC, it is possible without much risk to turn off the heart and lungs from work for several hours (and the surgeon has the opportunity to operate on the most complex defects).
✔ X-ray surgery appeared relatively recently, but, thanks to the incredible progress of modern technologies, they have already taken their rightful place in the arsenal of cardiac surgery. More and more doctors are now using thin catheters, the ends of which are fitted with balloons, patches, or expandable tubes (folded like a folding umbrella). With the help of a catheter, these devices are carried into the cavity of the heart, or into the lumen of the vessel, and then, expanding the balloon, break the narrowed valve with pressure, increase or create a defect in the septum, or, conversely, by opening the patch umbrella, this defect is closed. The tubes are inserted into the lumen of the desired vessel and create a wider lumen. In adults, they even try to pass an artificial aortic valve through the catheter in this way, but so far these are only attempts. Doctors monitor the course of an X-ray surgical operation on the monitor screen and clearly control all manipulations with the probe, and therefore the advantage of such operations is not only less trauma, but also high safety and efficiency. X-ray surgery has not yet supplanted traditional surgical methods, but it is gaining more and more space both as an independent method and as an “auxiliary”, i.e. which can be applied not instead of, but together with the usual operation, sometimes simplifying and supplementing it in many ways.
Depending on the type of defect and the condition of the child, surgical operations can be emergency, urgent and elective, i.e. planned.
emergency heart surgery are the ones that should be done immediately after the diagnosis is made, because any delay threatens the life of the child. With congenital malformations, such situations are not uncommon, especially when it comes to newborns. Here the question of life is often decided by hours and minutes.
Emergency operations- those for whom there is no such insane urgency. The operation does not need to be done right now, but you can calmly wait a few days, prepare both you and the child, but it must be done urgently, because then it may be too late.
Planned, or elective, operation- this is an intervention made at the time chosen by you and the surgeons, when the child's condition does not inspire fear, but the operation, nevertheless, should not be postponed.
No cardiac surgeon will ever suggest surgery if it can be avoided. So, anyway, it should be.
Depending on the approach to surgical treatment, radical and palliative operations are distinguished.
✔ Radical heart surgery is a correction that completely eliminates the defect. It can be done with an open ductus arteriosus, septal defects, complete transposition of the main vessels, abnormal pulmonary vein drainage, atrioventricular communication, Fallot's tetrad and some other defects, in which the heart is fully formed, and the surgeon has the opportunity to completely separate the circulatory circles, while maintaining normal anatomical relationships. Those. the atria will connect to their ventricles through correctly positioned valves, and the corresponding great vessels will depart from the ventricles.
✔ Palliative heart surgery- auxiliary, “facilitating”, aimed at normalizing or improving blood circulation and preparing the vascular bed for radical correction. Palliative operations do not eliminate the disease itself, but significantly improve the child's condition. With some very complex defects, which until recently were generally inoperable, the child will have one, and sometimes two palliative operations, before the final radical stage becomes possible.
During a palliative operation, another "defect" is surgically created, which the child does not initially have, but due to which the circulatory pathways disturbed by the defect in the large and small circles are changed. These include surgical expansion of the atrial septal defect, all variants of intervascular anastomoses - i.e. additional shunts, messages between circles. The Fontan operation is the most “radical” of all such methods, after which a person lives without a right ventricle at all. With some of the most complex heart defects, it is impossible to correct the anatomically, and surgical treatment aimed at correcting blood flow can be called the “final” palliative correction, but by no means a radical operation.
In other words, with heart defects, when the intracardiac anatomy - the structure of the ventricles, the condition of the atrioventricular valves, the location of the aorta and the pulmonary trunk - are so changed that they do not allow for a real radical correction, today's surgery follows the path of eliminating poorly compatible with life of circulatory disorders, and then - long-term palliation. The first stage of this path is saving lives and preparing for further treatment, and protection from future complications, the second is the final stage of treatment. All together - this is a long way to the final operation, and on it one, two, and sometimes three steps must be overcome, but, ultimately, to make the child healthy enough for him to develop, learn, lead a normal life, which this long-term palliation will provide him. Check it out, not so long ago - 20-25 years ago it was simply impossible, and children born with the defects of this group were doomed to death.
Such a “final palliation” is the only way out in many cases; although it does not correct the defect itself, it provides the child with an almost normal life by improving the mixing of arterial and venous blood flows, the complete separation of circles, and the elimination of obstructions to blood flow.
Obviously, the very concept of radical and palliative treatment for some complex congenital heart defects is largely arbitrary, and the boundaries are erased.
