How is the heart surgery going? The main types of surgical intervention on the heart. When is valve replacement necessary?
Such surgical manipulations are within the competence of cardiac surgeons, and are one of the most complex in nature. Heart surgery is a last resort in the treatment of serious cardiovascular diseases, which are resorted to in order to improve the quality of life of the patient, and sometimes even save his life.
In Russia, the type of surgical intervention in question is not practiced as often - as, for example, in America, or in European countries. First of all, this is due to the cost of such treatment: not every citizen of the Russian Federation is able to pay the costs of the operation out of his own pocket.
At the same time, this branch of medicine in domestic medical institutions constantly evolving, which enables patients to receive qualified advice and assistance when applying.
When is heart surgery performed - indications and timing
The main pathologies that may require surgical intervention are:
- Poor myocardial blood supply. Similar state in medical circles is called coronary heart disease. IHD can lead to the formation of an aneurysm, extensive thrombosis. With all the described ailments, certain surgical procedures on the heart may be required.
- Heart defects that have both innate and acquired nature. Many structural defects heart valve incompatible with life. Therefore, such pathologies are diagnosed even in the prenatal period, and the operation itself is carried out in the first days of the baby's life.
- Failures in the frequency, sequence and rhythm of heart contraction, - arrhythmias.
Common indications for heart surgery are the following pathological conditions:
- Active deterioration of vital signs against the background of the development of underlying heart disease.
- The inability of drug therapy to cope with the manifestations of the disease.
- Noticeable deterioration in the functioning of the heart muscle that cannot be eliminated with medications.
- advanced stage of the disease. This happens when the patient does not seek qualified help in time.
It should also be taken into account that any surgical manipulations on the heart carry a risk and are fraught with the development of a number of exacerbations in rehabilitation period. TO similar treatment doctors turn when other measures do not bring the desired effect.
In addition, heart surgery requires a comprehensive examination of the patient and careful preparation for the operation. This will ensure a successful recovery and minimize the likelihood of postoperative complications.
Based on the patient's condition, the type of surgical intervention under consideration is:
- emergency. In such a situation, examination and preparation are carried out in a minimal amount, and the operation itself is carried out in as soon as possible. This type of manipulation is prescribed for life-threatening conditions, when every minute counts: with aneurysm rupture, extensive myocardial infarction. Often emergency interventions on the heart is performed on a newborn with a complex heart disease.
- Urgent. There is time for diagnostic and preparatory measures, but not much. After receiving the results of the examination, surgical treatment of the heart disease is carried out.
- planned. In some medical sources, this type of operation is called elective. After detailed study condition of the patient, the cardiosurgeon finally decides on the need for surgical intervention. Together with the patient or his parents (when operating on a child), it is agreed exact date carrying out the operation.
Closed and open heart surgeries - how they are performed and to whom they are prescribed
Based on the type of defect to be eliminated, apply various methods surgical intervention:

Note!
Not so long ago, a new direction in the treatment of heart defects began to be applied in cardiac surgery - x-ray surgical operations . In essence, they are minimally invasive - the doctor makes small incisions or punctures, and brings special instruments to the heart zone through the catheter. An access point can be, incl. and femoral vessels. Using cans, you can increase the diameter of the narrowed valve - or reduce it by opening the patch (its design is similar to an umbrella). With the help of expanding tubules, vascular stenosis is eliminated.
The progress of the entire procedure is monitored through the monitor screen - this ensures the effectiveness of the operation, as well as its safety for the patient. In addition, during the considered manipulation general anesthesia does not use: the doctor is limited to anesthesia of mini-accesses.
X-ray surgery can be both the main and auxiliary methods of treating errors in the work of the heart.

Most popular types of heart surgery
To date, the following operations are used in cardiac surgery practice:
1. With coronary heart disease:

2. In case of diagnosing heart disease:

3. In the presence of arrhythmia:

In cases where the treatment of individual anatomical structures of the heart is impossible or ineffective, and main body for pumping blood cannot cope with its main function - they perform heart transplant .
This operation is fraught with a number of complications, among which is graft rejection.
Today, scientists are conducting research to maximize the life extension of those who have survived heart transplants.
Let's try to lift the veil of the mystery of their work and find out what types of heart surgeries exist and are carried out today. Is it also possible to perform heart surgery without an autopsy? chest?
When the heart is in the palm of your hand or open surgeries
Operations on open heart are called so because the cardiac surgeon "opens" the patient's chest, cuts the sternum and that's it. soft tissues performs an opening of the chest. Such interventions, as a rule, are performed with the connection of a heart-lung machine (hereinafter referred to as AIC), which is a temporary replacement for the heart and lungs of the operated person. This apparatus is a complex device of rather impressive dimensions, which continues to pump blood through the body when the patient's heart is artificially stopped.
Thanks to AIC, open-heart surgery can be extended for many hours if necessary. Open Operations used when replacing valves, coronary artery bypass grafting can also be produced in this way, many heart defects are eliminated by open interventions. It should be noted that AIC is not always used during their implementation.

Not always the body can tolerate the intervention of a foreign heart substitute: the use of AIC is fraught with such complications as kidney failure, violation of cerebral blood flow, inflammatory processes, disorders of blood rheology. Therefore, some operations on the open heart are carried out in the conditions of his work, without the connection of the AIC.
Such interventions on a beating heart include coronary artery bypass grafting, during this operation on a beating heart, the area of \u200b\u200bthe heart that the surgeon needs is temporarily switched off from work, and the rest of the heart continues to work. Such manipulations require high qualifications and skills of the surgeon, and also have a much lower risk of complications; they are perfect for people over 75 years old, patients with a large arsenal of chronic diseases, patients with diabetes than operations on an organ that is switched off from the blood circulation.
But all the pros and cons, of course, are determined by the cardiac surgeon. Only the doctor decides to keep the heart working, or stop it for a while. Open surgeries are the most traumatic, having a higher percentage of complications; after surgery, a scar remains on the patient's chest. But sometimes only such an operation can save a person's life, improve his health, return him to a full, happy life.
Intact heart or closed surgeries

If during surgical intervention there was no opening of the sternum, heart chambers and the heart muscle itself - then these are closed heart operations. During such operations, the surgical scalpel does not affect the heart, and the surgeon's job is to surgical treatment large vessels, cardiac arteries and aorta, the chest is also not opened, only a small incision is made on the chest.
Thus, a pacemaker can be installed, heart valve correction, balloon angioplasty, shunting, vascular stenting can be performed. Closed Operations less traumatic, have a lower percentage of complications, unlike open ones. Closed vascular surgery can often be the first step before subsequent heart surgery.
Indications for their conduct is always determined by the doctor.
Achievements of modern cardiac surgery or minimally invasive operations

Cardiac surgery is confidently moving forward, and an indicator of this is an increasing percentage of low-traumatic, high-tech manipulations that allow you to get rid of the pathology of the heart and blood vessels with minimal intervention and impact on human body. What are minimally invasive interventions? These are surgical operations performed by introducing instruments or special devices, through mini-accesses - 3-4 cm incisions, or without any incisions at all: during endoscopic operations incisions are replaced by punctures.
When performing minimally invasive manipulations, the path to the heart and blood vessels can lie through the femoral vessels, for example - these operations are called endovascular, they are performed under x-ray control. Elimination of congenital malformations, prosthetic heart valves, all operations on vessels (from removal of a blood clot to expansion of the lumen) - all these interventions can be performed using minimally invasive technologies. on them in modern cardiac surgery emphasis is placed on the fact that the low risk of complications, the minimal impact on the body are the huge advantages that patients can appreciate literally on the operating table.

Anesthesia during endoscopic procedures is not required, it is enough just to anesthetize the puncture site. Recovery after heart surgery performed using a minimally invasive technique is ten times faster. Such methods are also indispensable in diagnostics - coronary angiography, a method for examining the vessels of the heart by introducing contrast and subsequent x-ray control. In parallel with the diagnosis according to indications, the cardiac surgeon can also perform therapeutic manipulations on the vessels - the installation of a stent, balloon dilation in a narrowed vessel.
Both diagnosis and treatment by puncture on femoral artery? Isn't this a miracle? Such miracles for cardiac surgeons are becoming routine. The contribution of endovascular methods of treatment is also invaluable in cases where the threat to the life of the patient is especially acute and minutes count. These are situations of acute coronary syndrome, thromboembolism, aneurysm. In many cases, the presence necessary equipment and qualified personnel, allows you to save the life of patients.
When is the operation indicated?

It is up to an experienced cardiac surgeon or a council of doctors to decide whether an operation is indicated, as well as to determine the type of surgical intervention on the heart and blood vessels. The doctor can make a conclusion after a thorough examination, familiarization with the history of the development of the disease, monitoring the patient. The doctor must know the ins and outs of the disease very well: how long the patient has been suffering from heart disease, what medications he takes, what chronic diseases has, when he felt worse ... After evaluating all the pros and cons, the doctor makes his verdict: whether to have an operation or not. If the situation develops according to the above scheme, then we are dealing with a planned cardiac surgery.
It is shown to the following people:
- lack of effect from adequate drug therapy;
- rapidly progressive deterioration of well-being against the background of ongoing treatment with pills and injections;
- severe arrhythmias, angina pectoris, cardiomyopathy, congenital and acquired heart defects requiring correction.
But there are situations when there is no time for reflection, questioning and analysis of the medical history. We are talking about life-threatening conditions - a blood clot broke off, an aneurysm exfoliated, a heart attack occurred. When the time goes by for minutes, emergency cardiac surgery is performed. Stenting, coronary artery bypass grafting, thrombectomy can be performed urgently coronary arteries, radiofrequency ablation.
Consider the most common types of heart surgery

- CABG - coronary artery bypass grafting "on hearing" for many, probably because it is carried out with coronary disease heart, which is extremely common among the population. CABG can be performed both open and closed, and combined techniques with endoscopic inclusions are also performed. The essence of the operation is to create bypass routes of blood flow through the vessels of the heart, restoring normal blood supply to the myocardium, which leads to a better supply of oxygen to the heart muscle.
- RFA - radiofrequency ablation. This type of surgical intervention is used to eliminate persistent arrhythmias when drug therapy is powerless in the fight against arrhythmias. This is a minimally invasive intervention, which is performed under local anesthesia, a special conductor is inserted through the femoral or subclavian vein, supplying an electrode to the focus of pathological impulses in the heart, the current flowing through the electrode to the pathological focus destroys it. And the absence of a focus of pathological impulses means the absence of arrhythmia. 12 hours after the manipulation, the patient is already allowed to get up.
- Prosthetic or plastic heart valves. Prosthetics means complete valve replacement, the prosthesis can be mechanical or biological. And plastic implies the elimination of defects in the "native" valve or valve apparatus. There are certain indications for these interventions, which are clearly known to cardiac surgeons.
- Installing a pacemaker. Cardiac arrhythmias, severe bradycardia may be indications for installation, which, thanks to modern technologies can also be performed endoscopically.
God bless everyone long life so that his heart is never touched by the surgeon's scalpel. However, not always cardiac surgery can be replaced by therapy.
When is surgery necessary?
- When conservative therapy does not give the desired result.
- When, despite all the ongoing treatment, the patient's condition continues to deteriorate.
- When heavy birth defects heart, severe arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy.
By urgency, cardiosurgical operations are emergency and planned.
- Emergencies are carried out when a person's life is in serious danger. This happens when a myocardial infarction occurs, a blood clot suddenly breaks off, or aortic dissection begins. They do not tolerate delay in surgery when the heart is injured. The consequences of delay are severe.
- Planned are carried out in accordance with the developed plan for the correction of the patient's health. The date of the operation may be postponed depending on the circumstances. For example: with a cold, to avoid additional stress on the heart, or when the pressure suddenly dropped.
Surgical intervention differs in the technique of execution. There are such types of heart operations:
- with the opening of the chest;
- without opening the chest.
Chest opening operations
Such surgical intervention is used in especially severe cases, when full accessibility of the heart is required during the operation.
Opening of the chest is performed with such pathologies:
- tetralogy of Fallot (the so-called congenital heart disease with four serious violations of the anatomical structure);
- serious anomalies of intracardiac partitions, valves, aorta and coronary arteries;
- heart tumors.
The patient arrives at the hospital one day before the operation. Passes inspection, gives written consent. Need to wash antibacterial soap and shave your hair. Where do you shave your body hair? The hair will be shaved at the site of the proposed incision. If you are going to have a coronary bypass surgery, you will have to shave your legs and groin. In the case of a heart valve replacement, it is necessary to shave the hair in the lower abdomen and in the groin area.
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. To gain access to the heart, the surgeon opens the chest of the person being operated on. The patient is connected to an artificial lung ventilation apparatus, the heart stops for a while and surgical manipulations are performed with the organ.
How long the operation takes depends on the severity of the pathology. On average, several hours.
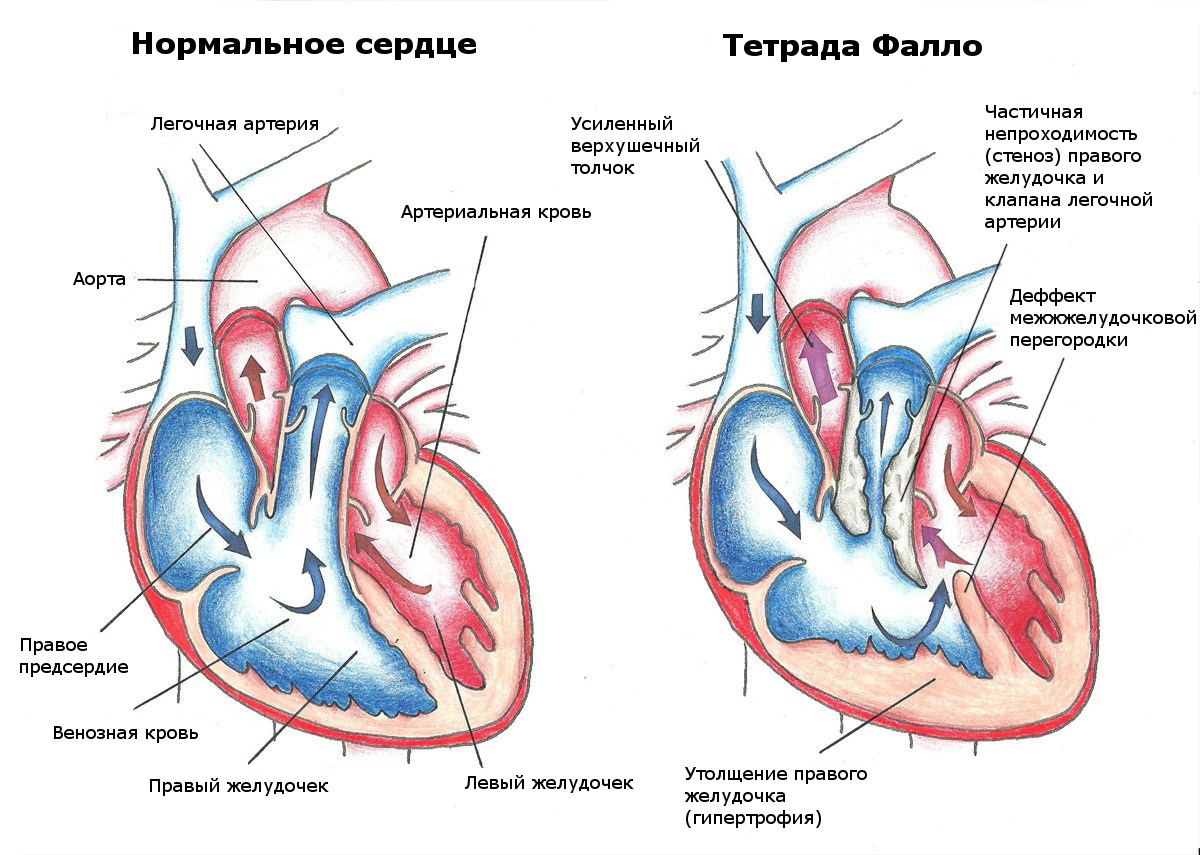 Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot Open heart surgery has two advantages.
- The surgeon has full access to the patient's heart.
- Such a surgical intervention is possible without state-of-the-art medical equipment.
However, there are also significant drawbacks.
- Surgical manipulations with the heart last several hours, which leads to fatigue of the operating team, during the operation there is a higher probability of making an erroneous action.
- Opening the chest is fraught with various injuries.
- There is a noticeable scar after heart surgery.
- Various complications are not excluded:
- myocardial infarction,
- thromboembolism,
- bleeding,
- infections;
- coma after surgery.
- A long recovery is required with significant limitations in the patient's activities.
In most cases, when surgery is performed with an opening of the chest, disability is given after heart surgery, as after a heart attack.
What operations and under what pathologies are performed on the open heart?
Pathologies of the coronary arteries
Coronary artery bypass grafting is done in case of serious atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary arteries, which led to a severe form of coronary heart disease. The essence of shunting is to create a bypass for blood flow to the heart using a shunt, for which an artery or vein taken from the patient is used. For example: mammary coronary artery bypass grafting (MCB) is performed using the internal mammary (mammary) artery.
 Operation Ross
Operation Ross Heart valve defects
These days, valves made from biological material patient.
- The Ross operation involves the use of one's own pulmonary artery a patient with a valvular apparatus to replace a pathologically altered aortic valve. An implant is placed in place of the pulmonary valve. Eliminates complications associated with rejection of a valve made of foreign material. Made for both adults and children.
- The Ozaki operation involves the use of the patient's own tissue. Only in this case, the replacement of the aortic valve is performed with a valve made from the patient's pericardium. Complications with valve rejection are not observed for the same reason.
Tuesday is surgery day. The team is preparing for a long morning work. During the operation, the chest is opened and the heart is prepared for vessel transplantation.
Disease history
Mr. Thomas, a 59-year-old tanker driver, is married with two adult children. He had shingles right side neck, and then there was an uncomfortable sensation of constriction in the throat, accompanied by sweating and nausea. He first felt these symptoms while walking up the steps of his truck. They continued, and Thomas decided to seek the advice of a therapist.Thomas's high blood pressure, obesity, and long history of smoking were reason enough for an ECG. Her results showed the presence of coronary heart disease. Thomas was referred to a cardiac expert (a cardiac internist, not a surgeon). Despite the applied drug treatment the pain continued.
Tests confirmed the presence of the disease, in particular an angiogram (a test using a dye injected into an artery to detect narrowing) revealed a narrowing in the left main coronary artery with damage to the left and right vessels. Since medical treatment was unsuccessful and angioplasty (stretching a narrowed vessel using a catheter) was not an option, Mr. Thomas was referred for surgery.
Monday
Mr. Thomas is hospitalized. His anamnesis, data of examinations and tests were analyzed. Two units of blood for transfusion are tested for compatibility. The patient is explained the essence of the operation and warned about the risk associated with it. Obtain written consent for CABG.Tuesday
Early in the morning, Mr. Thomas is being prepared for the operation.7:05 Premedication and anesthesia
8:15 Mr. Thomas had his sedation 70 minutes ago and the ventilation tube is already in his Airways. After the application of anesthesia and paralyzing agents, his breathing is supported by a ventilator. Prior to transferring Mr. Thomas to the operating room, the anesthesiologist establishes monitoring of venous and arterial blood flow.8:16 OR set up for Mr. Thomas. On the left - a table with instruments, on the right - a ready-to-use heart-lung apparatus.
8:25 Patient in the operating room. Skin his chest and legs are processed antiseptic solution to reduce the risk of infection.
8:40 Opening of the chest
The skin has already been processed, the patient is dressed in sterile clothes. One of the surgeons makes an incision in the leg to extract the vein, and the second cuts the skin on the chest. After a preliminary incision with an ordinary scalpel, he uses an electric one, which cuts the vessels, stopping the bleeding.8:48 The surgeon cuts the sternum bone with an electric saw with a pneumatic drive.
8:55 Artery and vein removal
View of the internal thoracic (mammary) artery in the mirror in the center of the surgical lamp. This artery is very elastic. The top end of it will remain in place, it will be cut off at the bottom and then connected to the coronary artery.An angled retractor is placed along the left edge of the sternum to lift it and expose the mammary artery that runs along inside chest.
At the same time, one of the main veins on the leg - the great saphenous vein - is prepared for transplantation. It is almost completely removed from the left thigh.
9:05 Connecting to the heart-lung machine
The heart-lung machine is not yet connected to the patient. One of the five rotating pumps circulates the blood, while the rest are used as side pumps to transport separated blood to prevent blood loss during surgery. The patient needs to enter heparin - a means to thin the blood and prevent the formation of clots during its passage through plastic tubes.Tubes to the heart-lung apparatus. On the left - with bright red blood - the arterial return line, along which blood is coming back into the patient's aorta. On the right - two tubes that drain blood from the inferior and superior vena cava under the influence of gravity. The incision in the sternum is fixed with a spacer.
Part of the heart-lung apparatus is a membrane oxygenating device that maintains blood circulation in the patient's body. IN this moment the device is filled with blood, carbon dioxide is removed from it. The blood is re-oxygenated and returned to the patient's body.
An arterial return tube is inserted into the aorta (the main artery of the body) and two venous drains are inserted into the vena cava (the main vein of the body).
9:25 Cardiac arrest
On the main artery - the aorta - a clamp is placed to isolate the heart from artificial blood circulation. Chilled fluid is injected into the isolated aorta to stop the heart. The surgeon puts on special glasses for microsurgery with loupes that give a magnification of 2.5 times. The blood vessels he will transplant are 2-3 mm in diameter, and the sutures are the diameter of a human hair.A thorough examination of the heart is carried out to confirm the data obtained using the angiogram. It is specified which coronary arteries need to be bypassed. It was decided to make two shunts.
After stopping the blood flow in the left anterior descending artery, a 1 cm long incision is made at the bypass site using a surgical loop.
10:00 First bypass
Close-up of the heart. The left internal mammary (mammary) artery - in the upper left corner - is sutured to the left anterior descending artery so that blood flow to the heart is restored. The arteries are hidden by epicardial fat.The end of the left internal mammary artery is sutured laterally to the left anterior descending artery. This forms the first bypass shunt.
The position of the first performed shunt. End of the lower part of the left internal mammary artery - blood vessel 3 mm in diameter - completely sutured to the left anterior descending artery.
10:22 Second bypass
The second bypass shunt is sutured with the upper end to the aorta, and with the lower end to the right posterior descending artery. The transverse clamp is removed, blood flow through the heart is restored.The upper end of the venous shunt is connected to the aorta. Part of the aorta is isolated with an arcuate clamp and a hole is made into which a vein is sutured.
End of both bypass processes. The second shunt, shown on the left side of the diagram, is formed from saphenous vein shins.
11:18 Chest closure
Circulation is restored, the heart contracts after an electric shock with the transition from ventricular fibrillation to sinus mode. Two drains are installed in the front and back parts hearts. The blood thinning effect of heparin was eliminated by the drug protamine. The surgeon sews the separated halves of the sternum together. The skin will be closed with an internal absorbable suture.The nurse applies tape to the suture and to the drainage tubes leading from the patient's chest. Soon the patient will be placed in the ward intensive care where it will be observed.
The human body. Outside and inside. №1 2008
How are operations performed?

An operation is an intervention in the human body with a violation of its integrity. Each disease requires an individual approach, which naturally affects the way the operation is performed.
How heart surgery is done: preparation for surgery
Heart surgery (cardiac surgery) is one of the most difficult to perform, dangerous and responsible type of surgical intervention.
Planned operations are usually carried out in the morning. Therefore, the patient is not allowed to eat or drink in the evening (for 8-10 hours), and immediately before the operation, a cleansing enema is given. This is necessary in order for the anesthesia to work as it should. 
The place where operations are performed must be sterile. In medical institutions, special rooms are used for these purposes - operating rooms, which are regularly sterilized by quartz treatment and special antiseptics. Moreover, the whole medical staff who takes part in the operation before the procedure is washed (you even have to rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution), and also changes into special sterile clothes, sterile gloves are put on your hands.
The patient is also put on shoe covers, a cap on his head, and the operation field is treated with an antiseptic. If necessary, before the operation, the patient's hair is shaved if the surgical field is covered with it. All these manipulations are necessary to avoid infection. surgical wound bacteria or other dangerous active microorganisms.
Narcosis or anesthesia
Anesthesia is a general anesthesia of the body with its immersion in drug-induced sleep.  At surgical interventions ah, general anesthesia is used on the heart, and in some cases, during endovideosurgical operations - spinal, in which a puncture is made in spinal cord at the level of the waist. Substances that cause pain may be administered different ways- intravenously, through the respiratory tract (inhalation anesthesia), intramuscularly or in combination.
At surgical interventions ah, general anesthesia is used on the heart, and in some cases, during endovideosurgical operations - spinal, in which a puncture is made in spinal cord at the level of the waist. Substances that cause pain may be administered different ways- intravenously, through the respiratory tract (inhalation anesthesia), intramuscularly or in combination.
Course of open heart surgery
After the person goes into medical sleep and ceases to feel pain, the operation itself begins. The surgeon uses a scalpel to open the skin and soft tissues on the chest. Cardiac surgery may also require an “opening” of the chest. To do this, with the help of special surgical instruments, the ribs are sawn. Thus, doctors “get” to the operated organ and put special dilators on the wound, which provide better access to the heart. Junior medical staff with the help of suction removes from operating field blood, and also cauterizes cut capillaries and vessels so that they do not bleed. 
If necessary, the patient is connected to the device artificial heart, which will temporarily pump blood through the body, while the operated organ is artificially suspended. Depending on what kind of heart surgery is performed (what kind of damage is eliminated), appropriate manipulations are carried out: it can be the replacement of blocked coronary arteries, the replacement of heart valves in case of defects, vein bypass surgery or the replacement of an entire organ.
Extreme care is required from the surgeon and all staff, as the life of the patient depends on it. It should also be added that during the operation, constant monitoring is carried out. blood pressure and some other indicators that indicate the patient's condition.
Endovideosurgery: stenosis and angioplasty
Today, more and more heart surgery is performed without open way- with a chest incision, and with access through the femoral artery on the leg, under the control of an X-ray machine and a microscopic video camera. After preparing for  operation, which is similar for all types of surgical interventions, and putting the patient into a medical sleep, access to the femoral artery is opened through an incision in the leg. A catheter and a probe with a video camera at the end are inserted into it, thanks to which access to the heart is provided.
operation, which is similar for all types of surgical interventions, and putting the patient into a medical sleep, access to the femoral artery is opened through an incision in the leg. A catheter and a probe with a video camera at the end are inserted into it, thanks to which access to the heart is provided.
In this way, angioplasty with stenosis of blood vessels is carried out in cardiac surgery, which is necessary for blockage of the coronary vessels that feed the heart itself with blood. Special stands are installed in the narrowed vessels - cylindrical implants that do not allow the arteries to clog anymore, which prevents the possibility of developing coronary disease.
After the main part of the operation is over and the heart is on its own again  functions, stitching of damaged nerves, vessels and tissues is performed. The wound is again treated with an antiseptic, the surgical field is closed, soft tissues and skin are sutured with special threads. A medical bandage is applied to the external wound. After the end of all these procedures, the patient is taken out of anesthesia.
functions, stitching of damaged nerves, vessels and tissues is performed. The wound is again treated with an antiseptic, the surgical field is closed, soft tissues and skin are sutured with special threads. A medical bandage is applied to the external wound. After the end of all these procedures, the patient is taken out of anesthesia.
Other types of transactions
Except abdominal operations described above, there are also operations performed in a less traumatic way:
- Laparoscopy - is performed using a laparoscope, which is inserted through 1-2 cm incisions in the skin. Most often used in gynecology, gastric resection and other operations in abdominal cavity. You can read more about this
- Laser surgery - is carried out using a special laser beam. Usually, operations are performed in this way on the eyes, when removing skin formations, etc. You can read more about the method
