Low density cholesterol is below normal. What is HDL cholesterol in a biochemical blood test. Preparation and procedure for testing
In the human body, cholesterol (also known as cholesterol) performs important role during metabolism, it is part of the structure of many cells of the body. However, there are “good” and “bad” fractions of this element, which have different effects on human health. With an increase in the amount of cholesterol in the blood, the risk of heart attack and stroke increases.
Increased lipoprotein cholesterol high density for dyslipidemia by inhibition of cholesteryl ester protein. Apolipoprotein E and atherosclerosis. Cubilin, high density lipoprotein receptor. Megalin acts in concert with cubilin to mediate the endocytosis of high-density lipoproteins.
High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in the Cardiovascular Equation: Still Considered "Good"? Effect of reciprocal inhibition of high-density lipoprotein oxidized low-density lipoprotein on endothelium-dependent arterial relaxation. How high-strength lipoprotein protects against the effects of lipid peroxidation.
What are high density lipoproteins
Most of the substance is produced by the body in the liver (about 80%), the remaining share comes from its intake with food. Cholesterol takes part in the formation of hormones, bile acids, and cell membranes. The element itself is poorly soluble in liquid, so for transportation, a protein shell is formed around it, which consists of apolipoproteins (a special protein).
What to do if your HDL cholesterol level is low
The influence of lipids and lipoproteins on thrombosis and rheology. Inhibition of endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression by high-density lipoprotein. Stimulation of endothelin-1 release by low-density and very low-density lipoproteins in cultured human endothelial cells. Stimulation of arterial cell prostacyclin synthesis using high-density lipoproteins.
Association between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and peripheral vasomotor function. Low and high density lipoproteins as mitogenic factors for vascular smooth muscle cells: individual, additive and synergistic effects.
This compound is called lipoprotein. Several types of it circulate through human vessels, which are different due to the different proportions of the elements included in the composition:
- VLDL - very low density lipoproteins;
- LDL – low density lipoprotein;
- HDL is a high density lipoprotein.
The latter contain little cholesterol and consist almost entirely of protein. The main function of HDL cholesterol is to transport excess cholesterol to the liver for processing. This type of substance is called good; it accounts for 30% of blood cholesterol. The excess of low density lipoproteins over high density lipoproteins provokes the formation cholesterol plaques, which, when accumulated in arteries and veins, lead to heart attack and stroke.
High-density lipoprotein and its apolipoproteins inhibit the cytolytic activity of complement. Research into the nature of the inhibitory part. International Prevention Task Force coronary disease hearts. Coronary heart disease: reducing risk. Scientific experience in primary and secondary prevention of coronary heart disease.
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults: Second Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults.
Blood test for cholesterol
To determine cholesterol levels, it is necessary to take a biochemical blood test that determines the content of HDL and LDL. Research is prescribed as part of a lipogram. It is recommended to do it to all people over 20 years old at least once every 5 years. If a patient is prescribed a low-fat diet or medications, blood tests should be taken more often to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel on Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of High-Dose Cholesterol in Adults. Evidence-based recommendations for prevention cardiovascular diseases among women.
Atherogenic lipoprotein phenotype: a proposed genetic marker for coronary heart disease. Imamura H, Teshima K, Miyamoto N, et al. Cigarette smoking, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol subfractions, and lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase in young women.
How to take it
Blood test for total cholesterol requires some preparation before taking it. To get the correct indicators, you must follow these rules:
- sampling should be carried out in the morning;
- limit fatty foods for 2-3 days before the procedure;
- last appointment food must be eaten 8 hours before the test;
- avoid physical activity, emotional stress;
- Stop smoking at least 30 minutes before the test.
Decoding

Effect of cigarette smoking cessation on lipid and lipoprotein profiles: a meta-analysis. Overweight body: an underestimated contribution to high blood cholesterol levels in whites American men. Lipoproteins, nutrition and heart disease. Low-intensity endurance training, plasma lipoproteins and the risk of coronary heart disease.
How to improve your lipid profile
Moderate alcohol consumption and reduced risk of coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis of effects on lipids and hemostatic factors. Effect of postmenopausal estrogen replacement on plasma lipid concentrations and lipoprotein metabolism. Effect of phenytoin on plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in men with low level high density lipoprotein cholesterol.
The test results show the total amount of cholesterol in the blood, the content of triglycerides, which affect lipid processes, and HDL, LDL. We can say that the ratio of bad and good cholesterol determines the likelihood of developing vascular diseases. This value is called the atherogenic index or coefficient. Otherwise, there is a specific list of indicators of the level of LDL and HDL in the blood of women and men of different ages:
High-density lipoproteins and atherosclerosis: the role of cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport. Low lipoprotein high density as a risk factor for coronary heart disease: report of the working group. Expert group on detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults. Third report of the National educational program on cholesterol.
Relation of cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein triglycerides to the incidence of atherosclerotic coronary disease. Low-density lipoprotein size, triglycerides, and high-density lipoproteins as risk factors for coronary heart disease in older Japanese American men.
| LDL cholesterol, mmol/l | HDL cholesterol, mmol/l |
|||
The atherogenic coefficient is increased
This conclusion, when deciphered, indicates the likelihood of developing heart disease, cholesterol plaques, and narrowing of the lumens of blood vessels, which leads to stroke and heart attack. In this case, “bad” cholesterol prevails over “good” cholesterol. To calculate the atherogenic coefficient, you need to subtract HDL cholesterol from the total amount of cholesterol and divide the result again by the HDL level. The reason for the development increased rate becomes:
Regression of atherosclerotic lesions by the high-density lipoprotein fraction in lactating rabbit cholesterol. Lipid-lipoprotein interactions with mortality from coronary heart disease in 19 countries. Cholesterol and lipids in coronary heart disease risk: the Framingham Heart Study.
Multi-Risk Research Group. Multiple risk factor intervention interventions: risk factor changes and mortality outcomes. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and coronary heart disease in people with hypercholesterolemia. Lipid Prevention Clinical Trials coronary arteries.
- severe liver disease;
- heredity;
- renal failure(chronic);
- undertreated diabetes;
- cholestasis;
- inflammation of the kidneys chronic form which leads to nephrotic syndrome.
Atherogenic coefficient is reduced
This good news, in this case, the risk of developing cholesterol plaques, blockages, heart attack or stroke is extremely small. This fact does not have any diagnostic value and means that there is high cholesterol HDL, which does not pose any danger to human health. During treatment, they always try to bring the atherogenic index to normal or lower it.
Predictive value of an exercise test in North American men: a postgraduate study. clinical trials lipids. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four promising American studies.
HDL deviations from the norm
Triglyceride concentrations and coronary heart disease. 8-year follow-up in the Copenhagen Men's Study. Epidemiological aspects of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The relationship between the level of high-density lipoprotein subfraction and the presence and degree of coronary artery disease.
HDL norm
Normal indicator not related to good cholesterol correct wording. The acceptable level of this fraction varies from case to case and is determined individually for the person. The likelihood of developing diseases of cardio-vascular system influenced by many factors that should be studied individually for each patient. Low HDL cholesterol definitely increases the risk of atherosclerosis. According to general statistics You can assess the risk of development in adults using the following indicators:
Low levels of high-density lipoprotein are associated with increased rates of restenosis after coronary angioplasty. Do ultra-low levels of low-density cholesterol provide additional benefits to the endothelium? "Clinicians" on lipids and coronary disease hearts. London: Chapman Hall Medical.
Reasons for increasing and decreasing HDL
Effects of dietary saturated fatty acid reduction on plasma lipids and lipoproteins in healthy subjects: Delta study protocol. Men and women differ in lipoprotein response to dietary saturated fat and cholesterol restriction. Effect of dietary fatty acids on high-density and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in healthy subjects.
- There is a high probability of developing atherosclerosis in men at 10 mmol/l, in women – 1.3 mmol/l, without taking into account associated factors.
- The average probability of atherosclerosis will be 1.0-1.3 mmol/l in men and 1.3-1.5 mmol/l in women.
- A person will have a low probability of atherosclerosis at 1.55 mmol/l.
How to increase good cholesterol if HDL is low
IN different periods a person may have different percentage HDL cholesterol. Therefore, a single blood test is not an indicator of the “usual” amount of cholesterol. This indicates the need to check the level of the substance regularly if there is a fear of an increase. Changes can occur over a short period of time, this is called fluctuations in cholesterol metabolism. To increase your HDL level you should:
National cholesterol education program diet versus a diet lower in carbohydrates and higher in protein and monounsaturated fat: a randomized trial. Is the diet optimal? low content carbs, low fat?
The influence of one, daily alcoholic drink on lipid and hemostatic markers of cardiovascular risk. Effects of weight loss on blood lipids and lipoproteins: a meta-analysis. Plasma lipoproteins and lipase and lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase activities in obese patients before and after weight loss.
- exclude corticosteroids, anabolic steroids, androgens;
- avoid stressful situations;
- take statins, fibrates, cholestyramine, phenobarbital, insulin, estrogens.
Find out more about how to get tested.
Video about bad and good cholesterol
Smoking, lipoproteins and cardiovascular disease risk: evidence from the Münster Heart Study. Effects on plasma lipoprotein of a sensible weight loss diet, with or without exercise, in overweight men and women. The effect of the amount and intensity of physical exercise on plasma lipoproteins.
Causes and dangers of changes in HDL in the blood
Regular physical exercise and a low-fat diet. Effect on the progression of coronary artery disease. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-raising high-density lipoprotein compounds: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
For patients at high risk of developing cardiovascular disease, an HDL cholesterol test is often ordered. What it is? This is what high density lipoproteins are called - chemical compounds cholesterol with proteins. HDL does not transport cholesterol from the liver to tissues, like low-density lipoproteins, but rather back to the liver, where it is broken down into fatty acid and prepares to leave the body.
Lipid changes and reduction in coronary heart disease in the Helsinki Heart Study. Are high-density lipoprotein and triglyceride levels important for secondary prevention? Prevention of coronary heart disease with pravastatin in men with hypercholesterolemia.
Effect of pravastatin on coronary events after myocardial infarction in patients with average cholesterol levels. Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study Group. Long-term intervention with pravastatin in the Coronary Disease Study Group. Prevention of cardiovascular events and death by pravastatin in patients with coronary artery disease and a wide range of initial cholesterol levels.
High-density cholesterol is considered “useful” because it eliminates excess cholesterol in tissues (including in vessels with atherosclerosis) and its natural removal from the human body. This means that a lack of HDL poses a risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies (in particular, the risk of the formation of atherosclerotic plaques).
Effect of pravastatin on coronary disease events in subgroups defined by coronary artery risk factors: a prospective pool design. Lipoprotein modifies and reduces the incidence of major coronary heart disease in the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study.
Video about high and low density cholesterol
Simvastatin and niacin, antioxidant vitamins or a combination for the prevention of coronary artery disease. Arterial biology for research therapeutic effects lowering cholesterol. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of extended-release niacin for progression of atherosclerosis in patients with secondary prevention who received statins.
HDL norm
There is no need to talk about a specific normal indicator, since the values differ significantly depending on the age group and gender of the patient. In children, the level of HDL is lower and, on average, is set at positions from 0.78 to 1.68 mmol/l. As for older people, their indicators can normally rise to 0.78 - 2.28. In most cases, a reading above 1 mmol/L is considered “good”, but again, characteristics may vary depending on a number of factors.
Randomized trial of a strategy to increase high-density lipoprotein levels; impact on progression of coronary heart disease and clinical events. A cholesteryl ester protein inhibitor attenuates atherosclerosis in rabbits. Intravenous injection Rabbit apolipoprotein inhibits the progression of atherosclerosis in rabbits fed cholesterol. Sydney Hornby specializes in metabolic diseases and reproductive endocrinology. He graduated from Claremont McKenna College and Drexel College of Medicine in Philadelphia, where he received his M.D. degree and worked for several years in academic medical research.
In women after 50 years, the level of high-density lipoproteins increases significantly and remains constantly higher than in men. This is considered normal.
Some features of HDL analysis
The material for the study is blood serum obtained during collection venous blood(most often from the veins of the elbow bend of the arm). In order to avoid wrong result analysis, it is necessary to exclude fatty foods, especially of animal origin, from the diet for several days. For some time before diagnosis, avoid excessive physical exertion and emotional stress. In addition, it is not recommended to smoke half an hour before the test.
According to the American Heart Association, the main source high cholesterol in the blood can be traced back to the saturated fat in your diet. Sunflower, olive, corn, soybean and canola oils with high content unsaturated fats. Plant sterols are cholesterol compounds that occur naturally in plants. The study evaluated 42 people over 80 weeks.
Procedure for conducting the study
Heavy cream, butter, cheese, whole milk, and products made with whole milk or shortening contain saturated fat. This blood test checks the cholesterol levels in your body. This is especially true if you have high triglycerides. You may need this test to find out how high your cholesterol levels are. High level Cholesterol is one of the things that can tell you how likely you are to get heart disease, so it's important to know your numbers.
Blood sampling is carried out strictly on an empty stomach; it is necessary to exclude food 12 hours before the examination.
Reasons for changes in HDL levels in the human body
Levels of high-density lipoprotein in the blood can vary significantly depending on diet, bad habits and the rhythm of the patient's life. Pathological reasons lower HDL are:
- illnesses endocrine system, in particular diabetes mellitus;
- damage to the coronary arteries (heart vessels);
- gallstones;
- pathologies of the liver and kidneys - nephrotic syndrome, chronic renal failure, cirrhosis, hepatitis;
- hyperlipoproteinemia type IV, hypertriglyceridemia;
- acute infectious diseases;
- hereditary diseases (for example, Tangier disease is a genetic pathology in which metabolism is disrupted).
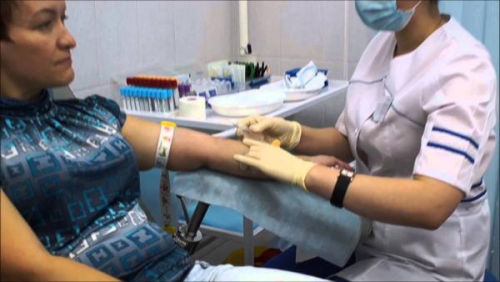
HDL levels may be lowered by taking a number of medicines: diuretics, beta blockers, hormonal drugs(androgens, progesterone). Severe stress and recent history can affect the results. infectious diseases. In these cases, they wait at least a month and a half to conduct the study.
Why might high-density lipoprotein levels be elevated? Very often this phenomenon is associated with intoxication of the body, including alcohol poisoning. In other cases, HDL may rise due to:
- chronic liver diseases;
- heavy physical activity;
- hereditary predisposition;
- alcoholism;
- biliary cirrhosis of the liver, etc.
In some cases, indicators increase due to treatment with medications: Phenobarbital and other antiepileptic drugs, estrogen, drugs with nicotinic acid. An increase in HDL levels is also observed during pregnancy.
When is systematic analysis necessary?
If there are a number of risk factors, it is worthwhile to constantly evaluate lipoprotein levels, making sure that they remain within normal limits. These factors include poor nutrition (or vice versa, some therapeutic diets), hypertension, previous myocardial infarction or stroke, history of coronary artery disease and diabetes mellitus, obesity, smoking and alcoholism, decreased physical activity.
It is recommended that patients older than 45 (for men) and 55 (for women) undergo HDL blood tests more often. If a close relative under 55 years of age (for the stronger sex) or 65 years of age (for the fairer sex) has had a heart attack or stroke in the family, it is extremely important to inform your doctor about this to determine the required frequency of testing. Similarly, children from 2 to 10 years old should be tested for high-density lipoproteins if their parents or immediate relatives suffered from high “bad” cholesterol.
How to increase HDL levels?
First of all, it is necessary, if possible, to exclude risk factors for the occurrence of cardiovascular pathologies. Of course, it is impossible to avoid heredity, but you can give up smoking and alcoholic drinks, exercise more often useful species sports - swimming, aerobics, therapeutic exercises.
It is also worth reconsidering your diet. It's best to exclude harmful products, especially those that contain a lot of animal fats. Such dishes are replaced with healthy ones: yoghurt, white bread, vegetables, legumes, potatoes, natural juices. It is very important to include in the diet fatty fish(salmon, tuna, sardines, herring, sea bass or mackerel), which has a high content of Omega-3 acids, which have a positive effect on the condition of the body as a whole and help restore HDL levels. To improve your condition, you need to eat fish dishes at least 2 – 3 times a week.
Remember that only a qualified specialist can correctly evaluate the results of a blood test for HDL and give comprehensive recommendations on further treatment and lifestyle. Do not self-medicate, value your health!
